Compressed Earth Block Construction
The modern descendent of the molded earth block, more commonly known as the Adobe Blocks.
Compressed Earth Blocks are construction materials made using damp soil under a high amount of pressure to form blocks. Compressed Earth Blocks (CEB) are like adobe bricks made from a mixture of sand clay and water. CEB is made from an earthen mixture and then compacted in a machine to form a block or brick. After compaction, they are cured for one or two days. CEB can be made at the site or can be transported to the site. Modern CEB are made using a machine. There are different types of machines available in the market that operates manually and electrically.
CEBs are made in-situ, reducing the carbon footprint. This also reduces the cost of manufacturing. CEBs are about 40% cheaper than conventional materials such as clay bricks. Due to their thermal mass quality, CEBs can save anywhere between 10-15% on cooling and heating costs. Also, the time required to manufacture these blocks is minimal. CEBs are approved construction materials and are widely popular in many countries like France, the UK, Germany, etc.

The materials that go into making CEBs come from nature. No chemicals are used in the making of these blocks therefore CEBs release no harmful or toxic gases.
There are two types of compressed earth blocks. Stabilized Compressed Earth Blocks and unstabilized Compressed Earth blocks. Stabilized compressed earth blocks are made by adding (5-7%) Portland cement in the earthen mixture. Stabilized Compressed Earth Blocks are widely used around the world.
Stabilized Compressed Earth Blocks:
Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks (CSEB), commonly called, Pressed Earth Blocks, are construction materials made using damp soil under a high amount of pressure to form blocks. They are composed of dry inorganic subsoil, non-expansive clay, aggregates, and Portland cement. CSEBs are an environmentally friendly alternative to clay bricks.
There are two types of Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks (CSEB).
- Interlocking compressed earth blocks (ICEB)
- Ordinary compressed earth blocks
Ordinary compressed earth blocks are simple blocks. They do not have grooves or joints in them. They are laid using mud mortar.
Interlocking Compressed Earth Blocks (ICEB):
Interlocking compressed earth blocks are composed of soil and cement. Adobe bricks and compressed earth blocks have been used as construction materials for centuries. More recently, interlocking compressed earth blocks have been used due to a few advantages they have over traditional smooth block construction. ICEBs have male and female appendages that make them easy to stack in a line, and holes that allow for both vertical and horizontal reinforcement. There are a different kind of interlocking patterns and each has a different use, the details of which is given below:
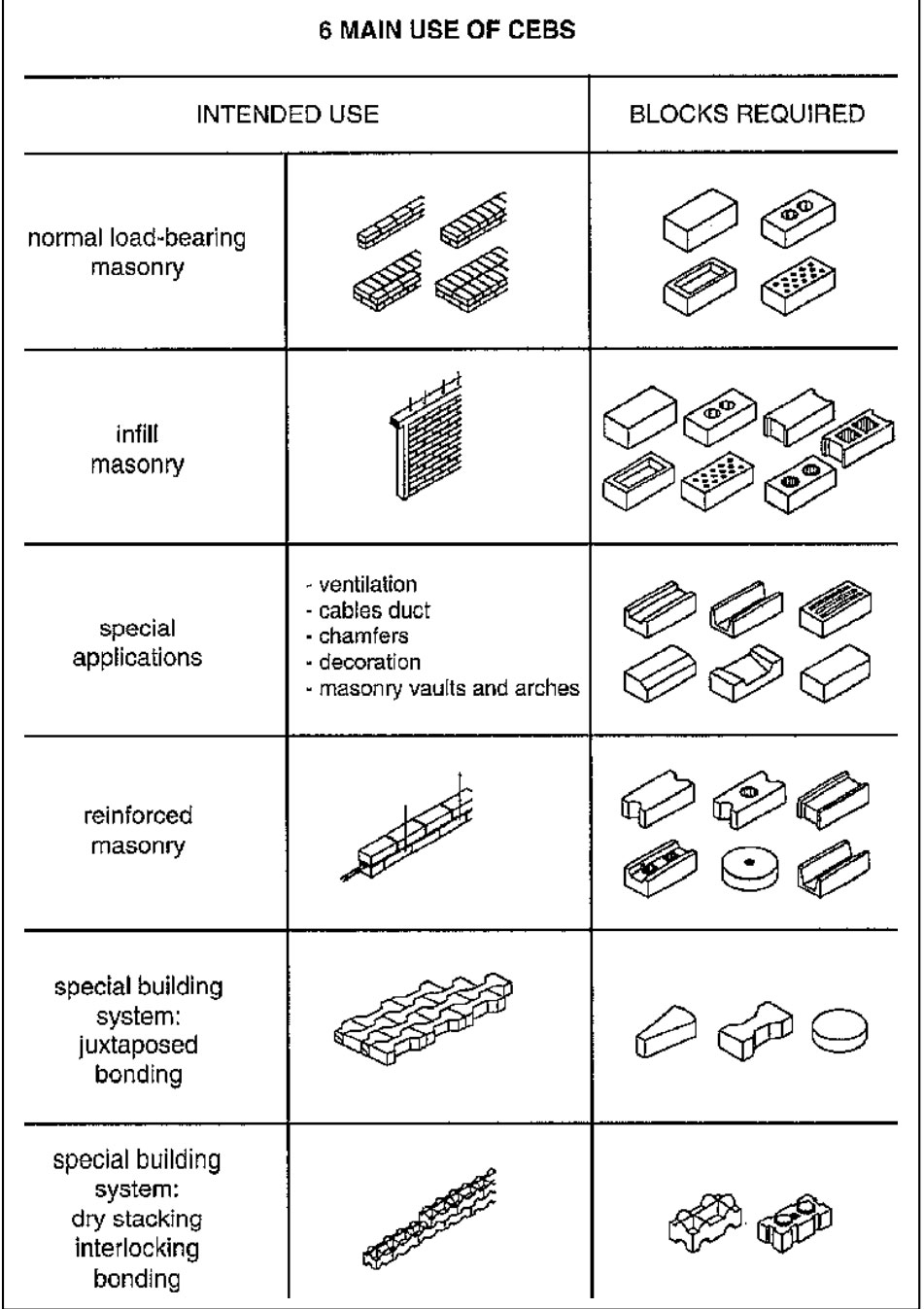
How To Make Interlocking Compressed Earth Blocks?
Since the desired soil properties are difficult to attain with just one sample, a combination of soils is typically used in ratios that provide for the strongest block. They can be made from any type of soil present in your surroundings. On-site tests can be done to ensure that a minimum of 15-30 percent of clay is present in your soil mixture. Sand, clay, cement, and water are mixed in a suitable proportion depending upon the type of soil available.
The general production process is discussed below:
- Add the cement to the earthen mixture and mix it thoroughly.
- Add a little water to the mixture. The mixture should be damp enough to clamp in the palm of the hands.
- Then the mixture is placed in the machine which compresses it and creates blocks.
- Then the blocks are dried and cured for a minimum of 2 days.
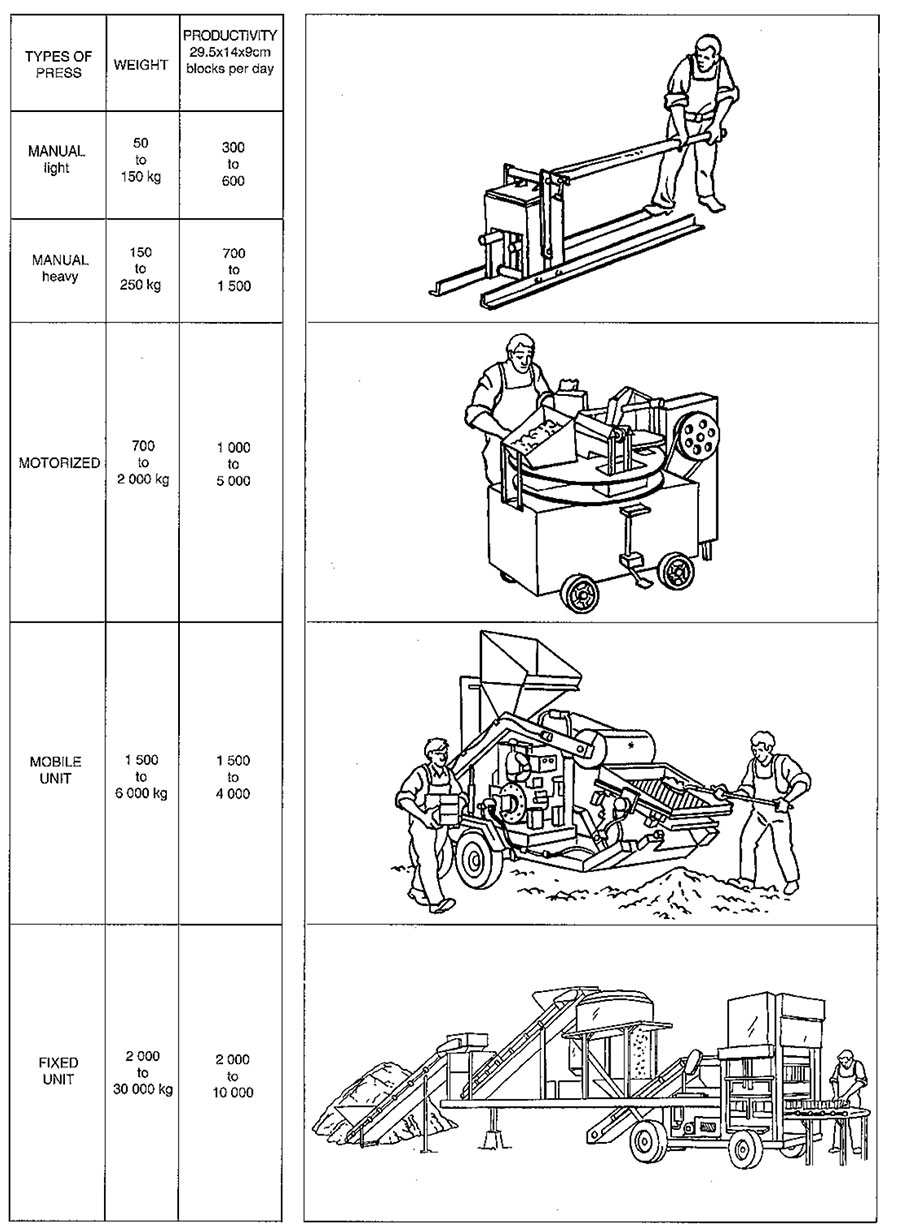
Compressed Earth Block Machinery:
There are different compressed earth blocks machines having different capacities and having different operating procedures. The manual earth block-making machines can only make one block at a time.
The automatic compressed earth block machine’s capacity varies from 100 to 300 blocks per operation. They are available in different price ranges and different operating power.
Types of Compressed Earth Block Machines:
Size of Interlocking Compressed Earth Blocks:
They are available or manufactured in different sizes according to its need. Usually, boundary walls and external walls are of more thickness. The nominal size for external and boundary walls blocks is 16 inches x 6 inches x 5 inches. The partition walls are of lesser thickness and the nominal size for partition walls blocks is 9 In. X 4 In. X 3 In.
How to Make a House with Compressed Earth Blocks(CEB):
CEB houses are constructed with CEB. The making of blocks is quite simple as compared to kiln brick and is discussed earlier. Once you have the compressed earth blocks, the process of making a house with them is quite similar to a simple masonry house. Simple CEBs are laid with mud mortar while interlocking CEBs are joined with respect to their male and female parts. Mud mortar is simply prepared by mixing some with soil. The walls of CEB houses are quite thick which is responsible for their excellent thermal insulation. The step-by-step guide to build your own house with CEBs is discussed below. Following these steps carefully, you can make your own sustainable house with your own barehand with the help of a few friends or you can hire professionals to do it for you.
Step 1: Preparation of site and layout of building:
Clean the site. There should be no grass or plants on the earth. Also, when you make adobe bricks, don’t use the topsoil material as it contains a lot of impurities. The mixture should be free from glass plastic large stones, small pieces of wood, roots, etc. Also, compress the site if necessary to avoid settlement in the future. Compressing on loose soil is mandatory Once the site is cleaned the next step is to make a layout of your building. Layout simply means transferring the walls from plan to site. Take a limestone powder and place it where your walls are going to be on the ground.
Step 2: Foundation:
Foundations are key to build a strong and durable house. Foundations of CEB structures vary from design to design. CEB walls are load-bearing walls. They have high thermal mass and are very thermally insulated. A simple single-story CEB building or house does not require any special foundations. The foundations of CEB walls can be made of brick ballast or gravel or stones if available. A rubble trench foundation can also be built under the CEB walls.
Step 3: Walls:
After the foundation has been completed, the layout for doors and windows, and block walls can begin. The compressed earth bricks are placed in accordance with the male and female parts of the brick. Windows and door frames are provided while constructing a wall. Door and window frames should be placed during the construction of the walls.


Step 4: Windows, Ventilator, and Door Frame:
The construction of CEB walls is very familiar to ordinary brick wall construction. In the case of interlocking bricks/blocks, care must be taken to interlock the male and female sides of the block. Like ordinary masonry construction, window and door frames are placed with a header or lintel extending 1ft beyond the width of the window and door.
Step 5: Roofing
Like any other natural earthen building, the roof of the CEB house can be made from wood. A simple wooden roofing system is employed. it is important to include a long sloping overhang on the south face of the roof of a CEB house built to capture passive solar energy to shade the many windows there during the summer months. In addition, extend the other roof(s) beyond the walls by at least 1 foot to move water away from the walls and foundation.
Step 6: Plastering
Since the CEBs are stabilized and they already have cement content in them, they don’t need plastering usually. But if you are in a region where heavy rainfalls are expected, a lime plaster should be done. Lime plaster is done in 2 coats having a thickness of 1.5” each.
Step 7: Flooring
Nobody wants to lay their feet on the uneven surface. The floor of the unfinished adobe house is just as same as the floor outside the building. So, we need to provide some kind of finishing to give it a proper surface. The ground is compacted a little bit and then plaster is applied on the ground. This plaster is done with a mixture of fine clay and water. After plastering, the surface is coated with linseed oil.
Making Compressed Earth Blocks – Youtube Video
Compressed Earth Block Machinery – Youtube Video
Trench Foundations – Youtube Video
Compressed Earth Blocks – Download PDF
Compressed Earth Blocks Construction (Whitepaper Explained in Urdu/Hindi) – Youtube Video




